deadlock definition: deadlock in os is a situation that occurs in OS when any process enters a waiting state because another waiting process is holding the demanded resource. Deadlock is a common problem in multi-processing where several processes share a specific type of mutually exclusive resource known as a soft lock or software.
Example of Deadlock
Deadlock meaning
A real-world example would be traffic, which is going only in one direction.
Here, a bridge is considered a resource. So, when Deadlock happens, it can be easily resolved if one car backs up (Preempt resources and rollback). Several cars may have to be backed up if a deadlock situation occurs. So starvation is possible.
What is Circular wait?
One process is waiting for the resource, which is held by the second process, which is also waiting for the resource held by the third process etc. This will continue until the last process is waiting for a resource held by the first process. This creates a circular chain.
For example, Process A is allocated Resource B as it is requesting Resource A. In the same way, Process B is allocated Resource A, and it is requesting Resource B. This creates a circular wait loop.
Example of Circular wait
One process is waiting for the resource, which is held by the second process, which is also waiting for the resource held by the third process etc. This will continue until the last process is waiting for a resource held by the first process. This creates a circular chain.
For example, Process A is allocated Resource B as it is requesting Resource A. In the same way, Process B is allocated Resource A, and it is requesting Resource B. This creates a circular wait loop.
Example of Circular wait
For example, a computer has three USB drives and three processes. Each of the three processes is able to hold one of the USB drives. So, when each process requests another drive, the three processes will have a deadlock situation as each process will be waiting for the USB drive to release, which is currently in use. This will result in a circular chain.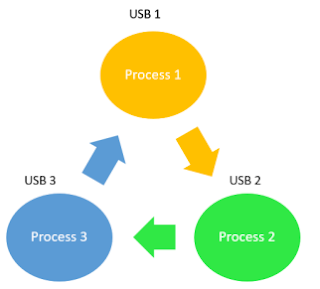
It is a set of methods for ensuring that at least one of the conditions cannot hold.
Methods for handling deadlock in os
- Deadlock detection & recovery
- Deadlock Prevention
- Deadlock avoidance (Banker's Algorithm)
- Deadlock Ignorance (Ostrich Method)
Deadlock Detection
A deadlock occurrence can be detected by the resource scheduler. A resource scheduler helps OS to keep track of all the resources which are allocated to different processes. So, when a deadlock is detected, it can be resolved using the below-given methods:Deadlock Prevention:
It’s important to prevent a deadlock before it can occur. The system checks every transaction before it is executed to make sure it doesn’t lead the deadlock situations. Even a small change occurs dead that an operation which can lead to Deadlock in the future also never allowed the process to execute.It is a set of methods for ensuring that at least one of the conditions cannot hold.
No preemptive action:
No Preemption – A resource can be released only voluntarily by the process holding it after that process has finished its task.If a process that is holding some resources request another resource that can’t be immediately allocated to it, in that situation, all resources will be released.
Preempted resources require the list of resources for a process that is waiting.
The process will be restarted only if it can regain its old resource and the new one that it is requesting.
If the process is requesting some other resource when it is available, then it was given to the requesting process.
If it is held by another process that is waiting for another resource, we release it and give it to the requesting process.
Resources shared such as read-only files never lead to deadlocks, but resources, like printers and tape drives, need exclusive access by a single process.
If the process is requesting some other resource when it is available, then it was given to the requesting process.
If it is held by another process that is waiting for another resource, we release it and give it to the requesting process.
Mutual Exclusion:
Mutual Exclusion is a full form of Mutex. It is a special type of binary semaphore used for controlling access to the shared resource. It includes a priority inheritance mechanism to avoid extended priority inversion problems. It allows current higher-priority tasks to be kept in the blocked state for the shortest time possible.Resources shared such as read-only files never lead to deadlocks, but resources, like printers and tape drives, need exclusive access by a single process.
Hold and Wait:
In this condition, processes must be stopped from holding single or multiple resources while simultaneously waiting for one or more others.Circular Wait:
It imposes a total ordering of all resource types. Circular wait also requires that every process request resources in increasing order of enumeration.Deadlock Avoidance:
It is better to avoid a deadlock instead of taking action after the Deadlock has occurred. It needs additional information, like how resources should be used. Deadlock avoidance is the simplest and most useful model in that each process declares the maximum number of resources of each type that it may need.Avoidance Algorithms
The deadlock-avoidance algorithm helps you to dynamically assess the resource-allocation state so that there can never be a circular-wait situation.A single instance of a resource type.
∙ Use a resource-allocation graph
∙ Cycles are necessary which are sufficient for Deadlock
Multiple instances of a resource type.
∙ Cycles are necessary but never sufficient for Deadlock.
∙ Uses the banker’s algorithm